In this edition, we'll be covering the following topics:
- ANSI A92 & CSA B354 Standard Changes.
- Mushroom farm fined $90,000 after worker critically injured by forklift.
- OSHA Raises Employer Penalties for 2019.
- Ask Bob: Our tech guru addresses a question on harnesses and lanyards.
- The Importance of Technician Training Programs.
- Drywall Contractor Fined $77,604 in Rough Terrain Forklift Incident.
- Last chance to register!
- What's Wrong With This? Photo and answer.
- A selection of interesting articles.
- New testimonials from our wonderful clients.
But first, check out all the places we are delivering training this month...
ANSI A92 & CSA B354 Standard Changes.
Machine Design Standard
ANSI A92.20 & CSA B354.6
This standard focuses on the design, calculations, safety requirements and testing methods for mobile elevating work platforms (MEWPs). It serves as a guide for manufacturers and engineers so they can build compliant machines.
What’s changed?
Load Sensing:
Machines are required to actively monitor loads and interrupt normal operations if they become overloaded.
Wind Force Requirements:
To be rated for outdoor use, machines may require reduced platform capacities and/or increased weight for more stability. Machines must be clearly marked if they are rated for indoor use only.
Tires:
Most rough terrain equipment will only be available with solid and/or foam-filled tires based on new stability testing guidelines.
Tilt Sensing Requirements:
Machines are required to have a tilt sensor alarm and may have a mechanism that disables certain boom functions if the incline surpasses the slope limit.
Folding Rails:
The railing height requirement has been raised for small indoor scissor lifts. Taller folding rails will replace fixed, non-folding rails on select models so they can fit through standard doorways.
Machine Markings & Documentation:
Machines must be clearly marked with the date of the last annual inspection and should have an updated manual on board that includes all new definitions and required information.
Who does it impact?
Manufacturers are impacted the most by these machine design changes. They have one year from the standards’ release date to bring their machines into compliance. Rental companies and dealers also need to be aware for training and servicing purposes.
For end users, changes like load sensing will require advanced planning because jobs that were previously done with overloaded machines will be impossible to complete with compliant equipment. They will need to carefully consider the application when choosing a MEWP for the job.
Safe Use Standard
ANSI A92.22 & CSA B354.7
This standard governs the safe use of MEWPs by specifying proper application, inspection, training, maintenance, repair and safe operation. One of the main requirements is developing a safe use program to guide MEWP use as it relates to job site safety.
What’s changed?
Step 1:
To develop an effective safe use program that complies with new requirements, it’s important to perform a site risk assessment before starting a job. This assessment should:
- Define the task, location and timing of the work
- Inform MEWP selection
- Evaluate MEWP-related, job-specific and additional risks
- Identify controls like proper training and rescue planning
Step 2:
Once a safety plan has been developed, it should be shared with everyone who will be on site during the work. The updated standards outline new requirements for many roles as they relate to a safe use program.
- Operator: Is trained and authorized to operate the MEWP
- Occupant: Has knowledge of MEWP use and safety, including fall protection systems
- Supervisor: Monitors use of MEWP to ensure safety plan is followed
- Technician: Performs MEWP maintenance in line with manufacturer’s requirements
Who does it impact?
This standard has the most impact on safety managers, supervisors and MEWP operators. Clear communication of the safety plan among all these parties is key to successfully meeting new safe use requirements. For rental companies, inspection and service records will be important to ensure a machine is compliant and safe to rent.
Training Standard
ANSI A92.24 & CSA B354.8
This standard focuses on training requirements. It provides guidance on preparing MEWP training materials, defines how theoretical and practical training should be delivered and identifies required elements for proper training and familiarization.
What’s changed?
According to the new standards, all training must be delivered by a qualified person who is experienced with the particular classification of MEWP on which training is being given. This qualified person must be knowledgeable about the laws, regulations, safe use practices, manufacturer’s requirements, recognition and avoidance of hazards as they relate to MEWPs.
While MEWP operator training is still mandatory, this requirement now extends beyond operators to include others who will come in contact with a MEWP on the job site, including:
- Supervisors: People who directly supervise MEWP operators (ANSI only)
- Occupants: People in the MEWP platform who are not considered operators (ANSI & CSA)
- Maintenance & Repair Personnel: People servicing MEWPs (CSA only)
Who does it impact?
This standard impacts both end users and dealers. Time should be allocated on the job site to account for additional training needs as they relate to supervisors and occupants.
Dealers are now required to offer training and familiarization to anyone who rents, leases or buys equipment. If requested, they must provide training or advise the renter on where to get training. They must also ensure that their maintenance technicians are properly trained on new features and marking standards.
Want more details? Our Essential Guide to Understanding ANSI & CSA Standard Changes outlines the new standards so you can work more and worry less.

Source: www.jlg.com
Mushroom farm fined $90,000 after worker critically injured by forklift.
 A Campbellville, Ont. mushroom farm has pleaded guilty to workplace safety violations after a pallet truck crashed with a forklift and hurt a worker.
A Campbellville, Ont. mushroom farm has pleaded guilty to workplace safety violations after a pallet truck crashed with a forklift and hurt a worker.
Monaghan Mushrooms Ltd. was fined $90,000 in a Burlington court this week. The company pleaded guilty to violating occupational health and safety laws at its growing facility at 7345 Guelph Line.
The incident happened on April 29, 2017. One Monaghan employee was driving a small mobile pallet truck, another a forklift.
The pallet truck driver was driving down a long indoor hallway to drop a skid of mushrooms in the pack house, the province says. The forklift driver was transporting mushroom tracks to a tray de-stacker.
Both spotted another forklift headed to the tray de-stacker, so they stopped and waited. Eventually, both started moving again and collided, according to the province. The pallet truck driver fell to the ground and was critically injured.
A Ministry of Labour investigation found the mushroom farm didn't have any policies, procedures or training around which vehicles have the right of way, the province says. All three workers had different ideas about who had the right of way.
This isn't the first time a worker was injured by a vehicle there, except the first time, the worker died.
On Dec. 20, 2011, a worker employed by a subcontractor was hit and killed by a reversing front-end loader. The province says Monaghan pleaded guilty then too, and was convicted on April 8, 2014 and fined $140,000.
In both cases, the province says, Monaghan violated section 25(2)(h) of the Occupational Health and Safety Act.
Justice of the Peace Paul Macphail issued the fine this week.
Source: www.cbc.ca
OSHA Raises Employer Penalties for 2019.
OSHA's civil penalties amounts for violations of workplace safety and health standards will increase in 2019 to adjust for inflation. The adjusted maximum penalty amounts will take effect upon publication in the Federal Register. New penalties for willful and repeat violations will be $132,598 per violation; serious, other-than-serious, and posting requirements are $13,260 per violation; and failure to abate violations are $13,260 per day beyond the abatement date.
Source: www.osha.gov
Ask Bob
Q. When do Narrow Aisle Order Picker Operators have to have their harness and lanyard connected to the equipment? Can they operate at ground level without being connected to the lanyard?
A. Great question and one I have argued with many operators!
As far as we are concerned, the moment you step on the platform, you tie off to the approved tie off point on the Order Picker.
People can always argue that they are not up in the air so legally OSHA does not require it. I play the devil’s advocate and then ask, “yeah, but what happens when you are just driving it and someone asks you to grab something real quick for them”. Next thing you know, the operator is ten feet up in the air with no harness and lanyard.
It’s just normal human behavior so I’ll stick to my convictions and tell everyone I train to tie off the minute they get on the platform.
The Importance of Technician Training Programs.
 Training in the aerial industry is very important - a life is at stake each and every time someone gets into a piece of aerial equipment. I don’t say this for dramatic effect, I say it because it’s true. Equipment operators depend on the aerial lift to work and function properly and safely every time they use it, for every job they do. Operators must be trained to operate the equipment properly. The more trained and qualified operators there are, the safer jobsites will be.
Training in the aerial industry is very important - a life is at stake each and every time someone gets into a piece of aerial equipment. I don’t say this for dramatic effect, I say it because it’s true. Equipment operators depend on the aerial lift to work and function properly and safely every time they use it, for every job they do. Operators must be trained to operate the equipment properly. The more trained and qualified operators there are, the safer jobsites will be.
Training goes beyond the operators. We also need to have technicians properly trained to work on, repair and maintain the equipment. Machines that receive the right care will run smoother, enhancing productivity on jobsites, while keeping operators safe. To make service and maintenance work more efficiently and help reduce downtime, technicians need to proficiently demonstrate the ability to calibrate, adjust and troubleshoot with the aid of available tools such as schematics, service manuals, laptop or table and connection software.
It is my goal to put the importance of training in a context everyone involved can understand. Think of it this way: We need to have qualified, knowledgeable and responsible technicians working on anything that holds a human in the air, right? To make sure of this, I always ask technicians I’m working with, “Are you comfortable with this repair?” They say, “Yes.”
And, I follow up with asking them, “Comfortable enough to put your child in it?” If they say yes again, I’m confident in what’s been done. But if they hesitate to answer or have second thoughts on the repairs, I know, and they know, we need to go back and keep working.
Why else is technician training important? Because it saves time and money.
Let me explain: A trained technician not only knows how to read the equipment schematics and how to do the repair, but that technician also knows how to get the repair done in the least amount of time with a minimal amount of parts expense, because it translates to less downtime for the machine and a higher return on investment for the company. For example, an untrained technician might take four hours and a lot of guesswork on which parts are needed to complete the repair. A trained technician may be able to do the repair in two hours, saving time, and with the right parts, saving money.
And, of course, there is the peace of mind knowing that equipment is properly maintained and in working order when it goes out to work on the next jobsite.
Source: www.aerialpros.genielift.com
Drywall Contractor Fined $77,604 in Rough Terrain Forklift Incident.
 WICHITA, KS – The U.S. Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has cited Midwest Drywall Company Inc. for safety violations after part of a forklift fatally crushed an employee at the company’s Wichita, Kansas, facility.
WICHITA, KS – The U.S. Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has cited Midwest Drywall Company Inc. for safety violations after part of a forklift fatally crushed an employee at the company’s Wichita, Kansas, facility.
The inspection revealed that a hydraulic boom hoist cylinder came free from the supporting slings, and landed on top of the employee. OSHA cited the company for serious violations of forklift, machine guarding, and control of hazardous energy standards. Proposed penalties total $77,604.
"Employers must take proactive steps to ensure that suspended and supported loads are properly secured at all times, and that employees are kept clear of such loads," said OSHA’s Wichita Area Director Ryan Hodge. "Companies should implement a comprehensive safety and health program that addresses recognition of hazards, safety precautions, and safety training."
The company has 15 business days from receipt of the citations and penalties to comply, request an informal conference with OSHA’s area director, or contest the findings before the independent Occupational Safety and Health Review Commission.
Under the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970, employers are responsible for providing safe and healthful workplaces for their employees. OSHA’s role is to help ensure these conditions for America’s working men and women by setting and enforcing standards, and providing training, education and assistance. For more information, visit https://www.osha.gov.
Source: www.osha.gov
What's Wrong With This? Photo
Can you tell what's going wrong in this photo?
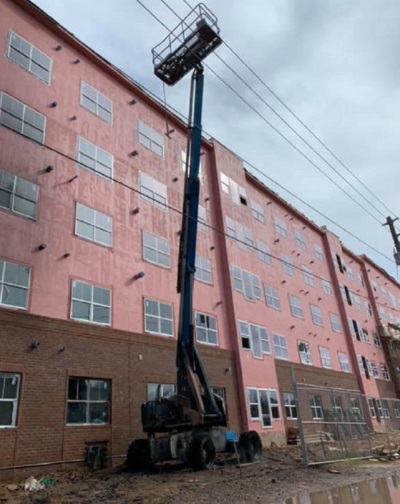

Have a photo you'd like to share? Send it to us!
Answer to Last Month's WWWT? Photo

Here's what our Director of Training, Rob Vetter had to say about it:
It looks like the decision makers at this worksite chose a rather risky-looking way to get their skid steer loader into a position where a crane could get to it and lower it down.
It’s pretty obvious by the downward angle or decline of the straining platform and the rickety-looking condition of the guardrails that it was not purpose-built for the task. It is also highly questionable as to whether it is actually rated for the weight of the unit it is supporting.
One shudders to think that at some point a live operator was also on the platform when it was driven off of the deck after being placed and back on to it for pickup – presumably.
Hopefully, the powers that be on this worksite will either find another way to get their loader where they want it to be or seriously overhaul the platform and re-engineer its supporting structure such that it is safe, secure and rated for the task.
Have a photo you'd like to share? Send it to us!
Interesting Articles
Seven-year-old girl dies in Taiwan forklift accident...more.
VIDEO: Unpaid construction worker destroys Travelodge entrance with an excavator...more.
Dehydration danger: should all forklifts come with cupholders?...more.
Firefighters rescue worker buried in collapsed hole dug by an excavator...more.
VIDEO: Volvo skid steers play soccer...more.
Contractor cited $57,463 for exposing workers to trenching hazards following fatality...more.
Tulameen man seriously injured in excavator crash...more.
Forklift operator rescued after 140,000 pound forklift sinks in ocean...more.
Man freed after his foot was pinned under excavator...more.
VIDEO: Sinkhole swallows loader and its driver in Ventura County...more.

Client Testimonials
"This class was hands down the most thorough and complete class I’ve ever taken. I was able to fully grasp concepts I previously had been trained on but did not understand." Tim, Converge Engineering.
"This program was amazing & should be required for trainers who sincerely care about their company & employees." Dustin, Motive Energy.
"It is a very structured and organized method that gives me the tools to become a competent trainer." Russell, Safety Russell.
Did you enjoy this newsletter? Sign up for our newsletter to receive more like this!